07 November 2023
SafeAeon Inc.The internet connects us all. It's crucial for society and business alike. But as our world grows more connected, protecting our online networks is more important than ever. Network engineers, designers, lawmakers, and enforcers face a huge challenge. They must keep the internet safe from crimes, hacking, and attacks. Fortunately, we have many options for safeguarding our networks. There is no such thing as a safe network without a firewall. Based on security policies, they track and manage all network traffic. Firewalls can either protect an entire network or individual computers. Network firewalls can be software or hardware-based and filter traffic between networks. Host-based firewalls are software layers on a single host that control network traffic in and out of that machine. Some firewalls also offer extra features, like acting as a DHCP or VPN server.
The Network Security Architecture Diagram is another vital tool. It shows the network's structure and the actions taken to secure it. This diagram can be created with software resources and hardware devices. If you've ever dreamed of finding powerful software to help design a Network Security Architecture Diagram, you're in luck. The market is full of great options that cater to various needs and preferences.
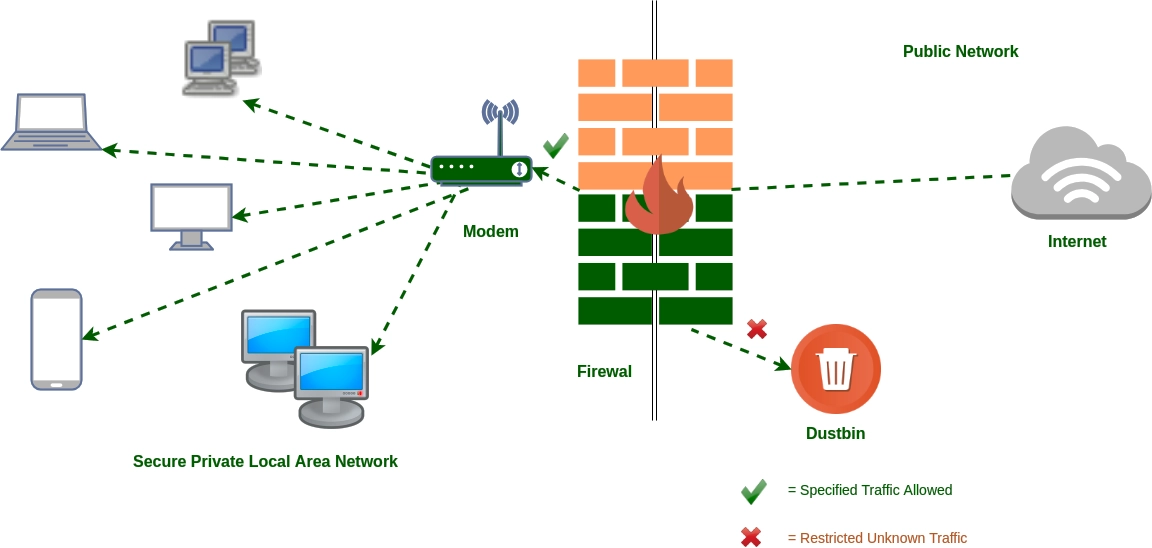
What does a network firewall do?
A network firewall is a watchdog for inbound and outbound traffic. It scrutinizes IP addresses, communication protocols, content types, and other traffic traits. After analyzing these aspects, it either blocks or allows traffic per established policies.
Firewalls are essential for meeting various security, privacy, and compliance requirements. In the U.S., the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) mandates network firewall security. Similarly, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a globally recognized mandate.
How does a network firewall work?
Network firewalls function by enforcing policies through access control mechanisms. These can include defined policies, allow/deny rulesets, and other guidelines. They determine how traffic should be handled based on its characteristics.
Firewalls analyze data within the four Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) communication layers. These layers are, from highest to lowest: application, transport, IP/network, and hardware/data link. These TCP/IP layers are the roadmap for moving data from its origin to its destination. The more advanced the firewall, the better it is at managing traffic effectively. This enhanced ability to gather information allows for more detailed traffic controls and comprehensive accounting.
Benefits of network firewall security:
- Enforce access privileges to minimize risk. Network firewalls are great for maintaining a Zero Trust security architecture. They do this by only allowing traffic that has express permission to pass. In other words, they "deny by default".
- Limit access to confidential resources. With a network firewall in place, unauthorized users won't be able to access sensitive data. This includes important information like patient records and financial details.
- Protect against cyber threats. Network firewalls are our first line of defense against cyber attacks. They block and prevent threats that can come from malware or malicious websites. This is especially important for stopping attacks that target users within your organization.
A Simple 5-Step Guide to Configuring a Firewall: Creating a Firewall Diagram
There are plenty of excellent firewall models that can help safeguard your network. To find the best one for your needs, consider consulting a HIPAA or PCI security expert. They can provide valuable insights tailored to your situation. Once you've selected a firewall, the next steps are crucial, no matter which model you choose. This guide is designed for those using a business-grade firewall that supports multiple internal networks (or zones) and performs stateful packet inspection. But don't worry!
Here were provide some general direction to help illustrate the process.
This way, you'll have a clear understanding of the 5 steps required to configure your firewall.
Step 1: Secure your firewall
Network security is crucial, and the first step in achieving it is by securing your firewall. If an attacker gains administrative access to your firewall, they can compromise your entire network. So, it's essential to take the following steps:
- Update your firewall's firmware to the latest version.
- Remove or disable default user accounts. Make sure to change all default passwords to complex and secure ones.
- If many administrators control the firewall, create extra accounts with limited access. Never log onto a computer with someone else.
- You should either prevent SNMP from running or set up a password-protected community string for it.
Step 2: Organize your firewall zones and IP addresses
Identify the valuable assets on your network. Examples include payment card data or patient data. Next, plan out your network's structure. The goal is to group assets based on sensitivity and function, placing them into specific networks or zones. Here's a breakdown:
- Internet-facing servers, such as web and email servers, should go into a dedicated zone. This is often referred to as a demilitarized zone (DMZ). The DMZ restricts inbound internet traffic.
- Servers that shouldn't have direct internet access, like database servers, belong in internal server zones.
- Workstations, point-of-sale devices, and VOIP systems usually go in internal network zones.
More zones generally mean better security. However, managing multiple zones can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. So, carefully consider the number of zones you need.
For those using IP version 4, all internal networks should have internal IP addresses. Network Address Translation (NAT) should be configured to allow internal devices to communicate online when necessary.
Once your network zone structure and IP address scheme are ready, create your firewall zones. Assign them to your firewall interfaces or subinterfaces. Lastly, use switches that support Virtual LANs (VLANs) to maintain separation between networks.
Step 3: Configure access control lists.
Start by determining the necessary traffic flow into and out of each network zone. Use firewall rules called access control lists (ACLs) to permit this traffic. Apply ACLs to each interface or subinterface on your firewall. Make ACLs as specific as possible, specifying source and destination IP addresses and port numbers. Always include a "deny all" rule at the end of each ACL to filter out unapproved traffic. Apply inbound and outbound ACLs to each interface and subinterface to ensure only approved traffic enters and exits each zone.
For added security, disable public access to your firewall administration interfaces, such as secure shell (SSH) and web interfaces. This protects your firewall configuration from outside threats. Also, disable all unencrypted protocols for firewall management, including Telnet and HTTP connections.
Step 4: Configure your other firewall services and logging.
If your firewall can act as a DHCP server, NTP server, intrusion prevention system (IPS), etc., configure the services you want to use. Disable any unnecessary extra services. For PCI DSS compliance, configure your firewall to report to your logging server. Ensure your logs include enough detail to meet requirements 10.2 through 10.3 of the PCI DSS.
Step 5: Test your firewall configuration.
Start by verifying your firewall works as intended in a test environment. Check that it blocks traffic as per your Access Control List (ACL) configurations. Your test should include vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
After testing, your firewall should be production-ready. Don't forget to back up your configuration in a secure place to avoid losing your hard work due to hardware failure.
Keep in mind, that this overview is to help you understand the main steps in firewall configuration. Whether you follow tutorials or configure the firewall yourself, have a security expert review your setup. This ensures your data is as protected as possible.
Conclusion
A firewall diagram is a key tool in understanding network security. It visually lays out the relationships and interactions between network zones and firewall rules. This clarity is essential when it comes to deciphering the complexities of network security policies and how they are implemented.
A firewall diagram does more than just show traffic flow. It also highlights potential security vulnerabilities. This ensures you have the right protections in place. It's important to identify your network zones, map out traffic flow, and define your access control lists. The goal is to make a diagram that's detailed enough to provide a full picture of your network's security. Yet simple enough that even those without a technical background can understand it.
A well-made firewall diagram is invaluable. It's not helpful for maintaining and troubleshooting your network. It's also a vital resource during security audits and compliance checks. Taking the time to create a user-friendly, accurate firewall diagram is a smart move for anyone who wants to boost their network security. It's an investment that pays off by protecting your data and resources. By getting in touch with MSSP like SafeAeon you can strengthen network performance.